Discuss the Five Pillars of Islam’ The Bedrock of Islamic Practice
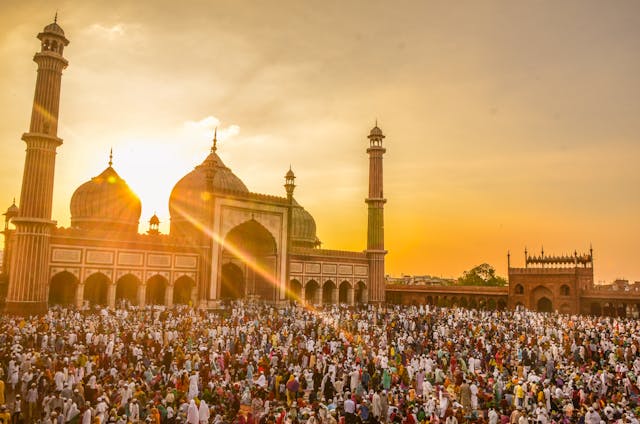

Islam, one of the world’s major religions, is anchored on five fundamental pillars that serve as the cornerstone of its practice.
These pillars transcend geographical, ethnic, and sectarian boundaries, uniting Muslims worldwide in their faith and devotion.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the significance of each pillar, its practical implications, and the challenges faced in upholding them in diverse contexts.
The Five Pillars: Bedrock of Islamic Practice
**1. ** Shahada: The Declaration of Faith
At the heart of Islamic belief lies the Shahada, a profound declaration affirming the oneness of God (Allah) and the prophethood of Muhammad.
Uttered by Muslims worldwide, it serves as a testament to their unwavering faith and allegiance.
Despite its association with extremist groups in the Western media, the Shahada holds deep spiritual significance for Muslims, marking the threshold of conversion and initiation into the Islamic faith.
**2. ** Salah: The Ritual Prayer
Salah, or ritual prayer, stands as a cornerstone of daily worship for Muslims. Observing Salah five times a day, Muslims align themselves with the divine will, seeking spiritual nourishment and guidance.
Yet, this sacred act of devotion has been marred by acts of terrorism, as witnessed in the targeting of congregational prayers by extremist factions.
The tragedy of bombings in mosques serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of places of worship in the face of violence.
**3. ** Zakat: Alms-giving
Central to Islamic ethics is the concept of Zakat, or almsgiving, which underscores the importance of charity and compassion towards the less fortunate.
Muslims are obligated to give a portion of their wealth to those in need, fostering social solidarity and addressing economic disparities within society.
However, the equitable distribution of Zakat remains a challenge in many Muslim-majority countries, where poverty and inequality persist despite religious injunctions.
ALSO READ: What Was The Oldest Religion in the World
**4. ** Sawm: Fasting during Ramadan
The sacred month of Ramadan is marked by fasting (Sawm), during which Muslims abstain from food, drink, and worldly pleasures from dawn till dusk.
This spiritual discipline fosters self-reflection, empathy, and gratitude, while also promoting physical and mental well-being.
Despite its profound spiritual benefits, observing Sawm amidst the demands of modern life can be daunting, with factors like work commitments and health considerations posing significant challenges.
**5. ** Hajj: The Pilgrimage to Mecca
Hajj, the pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca, represents the culmination of a Muslim’s spiritual journey.
Every year, millions of pilgrims from diverse backgrounds converge upon Mecca, reaffirming their faith and unity in the presence of God.
However, logistical constraints, health concerns, and geopolitical tensions often hinder the fulfillment of this sacred obligation, underscoring the complexities of contemporary pilgrimage.
Conclusion
In essence, the five pillars of Islam encapsulate the essence of Muslim identity and practice, serving as a timeless guide for spiritual fulfillment and moral conduct.
Despite the challenges and obstacles encountered in upholding these pillars, Muslims worldwide continue to draw strength and inspiration from their faith, reaffirming their commitment to the path laid down by the Prophet Muhammad.
For further insights into Islam and its teachings, visit reputable sources such as Islamicity and Islamic Relief.